DNA paternity testing has revolutionized the way we establish biological relationships. It is a scientific method that provides an accurate means of determining whether a man is the biological father of a child. With advancements in genetic technology, these tests have become more accessible and reliable, offering peace of mind to those seeking clarity regarding paternity. This article breaks down the foundational concepts of DNA paternity testing, the processes involved, how genetic markers are analyzed, and how to interpret the results.
Understanding the Basics of DNA Paternity Testing
DNA paternity testing is grounded in the principles of genetics, which is the study of heredity and variation in living organisms. Every individual inherits half of their DNA from their mother and half from their father. This unique combination of genetic material can be analyzed to confirm biological relationships. The test compares specific segments of DNA collected from the potential father and the child, focusing on the markers that indicate their biological connection.
There are two primary types of DNA tests utilized for paternity testing: the legal test and the non-legal test. The legal test often involves a chain of custody, ensuring that samples are collected and handled in a way that maintains their integrity for use in court. Non-legal tests, often referred to as at-home tests, are designed for personal knowledge and are less formal, lacking the rigorous protocols of the legal variety. Regardless of the type, the underlying science remains the same.
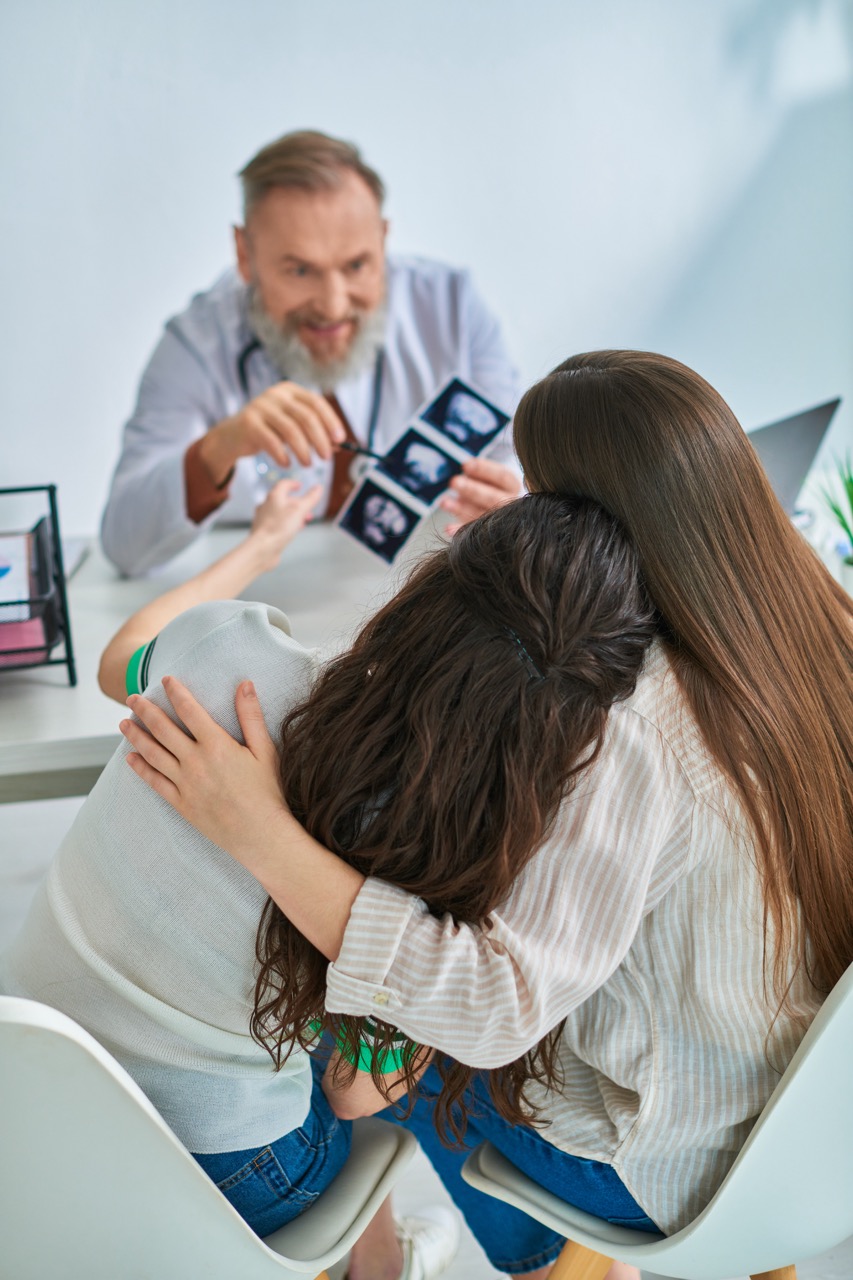
Understanding the significance of DNA testing extends beyond mere curiosity; it can have profound emotional, legal, and financial implications. Establishing paternity can influence child support, custody arrangements, and inheritance rights. Therefore, many individuals seek these tests not just for closure, but also for navigating complex family dynamics and legal matters.
The Process: Sample Collection and Preparation
The first step in the paternity testing process is sample collection. Typically, buccal swabs—cotton swabs rubbed against the inside of the cheek—are used to obtain DNA samples. This method is quick, painless, and non-invasive, making it the preferred choice for both children and adults. In some cases, other biological samples such as blood or hair follicles may be collected, but buccal swabs are most common due to their ease of use and effectiveness.
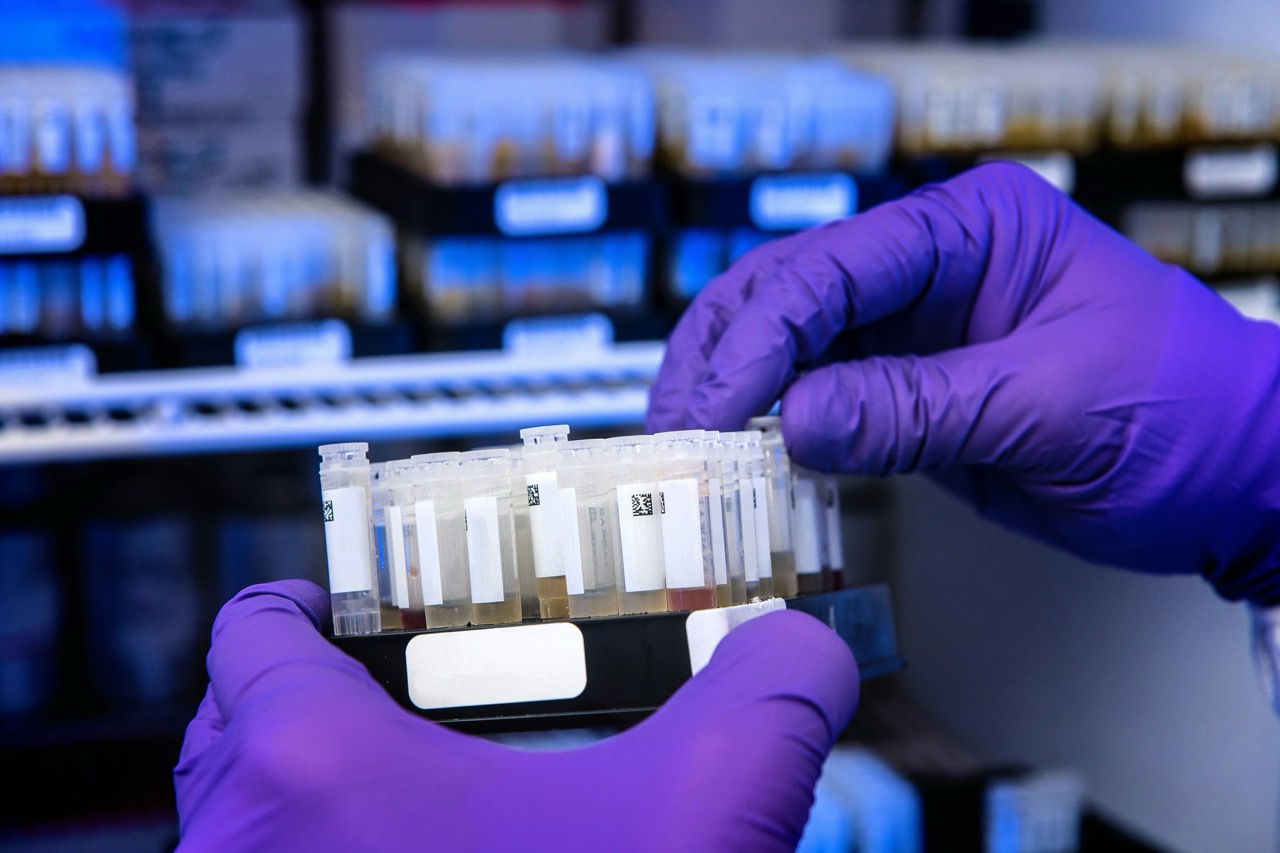
Once samples are collected, they are sent to a laboratory where they undergo preparation for analysis. In a lab setting, the DNA is extracted from the cells obtained in the swabs. This extraction process provides the genetic material necessary for subsequent testing. The samples are then quantified to ensure adequate DNA is present for analysis, as insufficient quantities can yield inaccurate results or prolonged processing times.
Quality control is vital during this stage to prevent contamination or degradation of samples. Laboratories utilize strict protocols to maintain sample integrity and ensure accurate results. It is essential that both the child’s and the alleged father’s samples are handled with care, and the identities are carefully preserved to avoid any potential mix-up or errors in testing.
Analyzing Genetic Markers for Paternity Verification
After sample preparation, the next phase involves analyzing specific genetic markers that can indicate paternity. DNA consists of numerous sequences known as loci, and these loci are where genetic variation can be observed. In paternity testing, laboratories typically examine between 15 to 20 loci to establish a comparison between the child’s and the alleged father’s DNA.
Each locus contains variations known as alleles, which can be inherited from both parents. For example, if a child has an allele at a given locus that is also present in the alleged father, this suggests that he may indeed be the biological parent. Conversely, if there are alleles present in the child that cannot be matched to the father, this suggests a lack of biological relationship. The more loci that are tested, the higher the accuracy of the results, with most modern DNA paternity tests providing an accuracy rate of 99.9% or higher when paternity is confirmed.
The analytic techniques used by laboratories may include Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) and Short Tandem Repeat (STR) analysis. These advanced methods allow for the amplification and examination of specific DNA sequences, yielding detailed profiles that can be compared for paternity verification. As technology advances, the precision and reliability of these tests continue to improve, making them a cornerstone of modern genetic analysis.
Interpreting Results: Accuracy and Implications
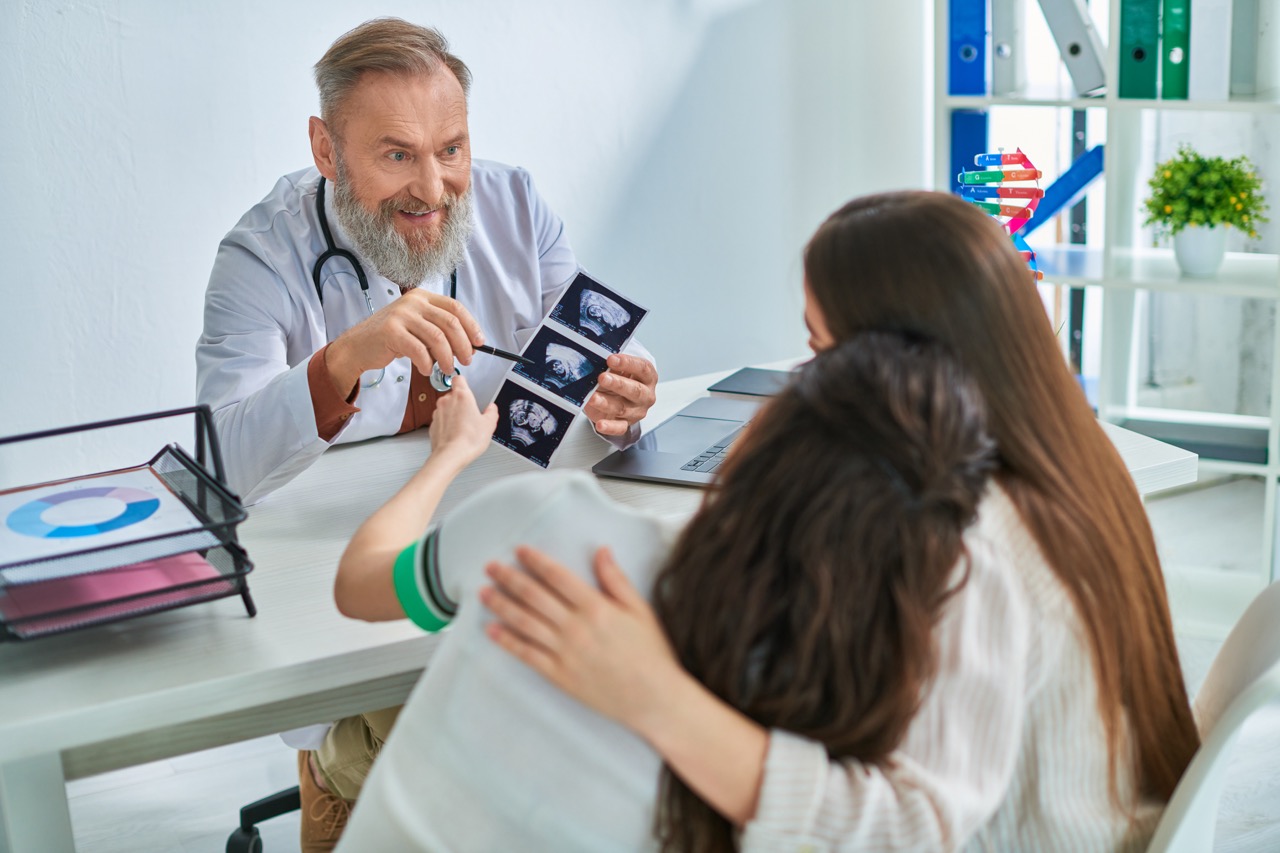
Once the analysis is complete, the results are compiled into a report that outlines the findings of the paternity test. Typically, the report will indicate whether the alleged father is excluded as a biological parent or if there is a degree of probability associated with a positive result. A probability of 99.9% or higher generally confirms paternity, while a lower percentage indicates that the alleged father is not the biological parent.
Interpreting these results can be emotionally charged and can have significant personal implications. For some, confirmation of paternity can strengthen familial bonds, while for others, it may raise questions about relationships and trust. Additionally, the results can inform legal matters, such as child custody, inheritance disputes, and child support obligations, necessitating a careful examination of the outcomes.
It is crucial for individuals receiving paternity test results to consider seeking professional guidance, especially if the results prompt emotional distress or complex legal issues. Counselors, geneticists, or legal professionals can provide support, ensuring that parties are equipped to handle the ramifications of the results and navigate any subsequent actions that may be required.
DNA paternity testing serves as a vital tool for clarifying biological relationships, offering a reliable method for individuals seeking answers about paternity. By understanding the foundational principles, processes involved, and the implications of the results, individuals can make informed decisions based on scientific evidence. As technology continues to enhance the accuracy and reliability of these tests, the potential for resolving personal and legal matters through DNA testing will only expand, underscoring the importance of genetic understanding in today’s world.