Non-Invasive Prenatal Paternity Testing (NIPPPT) has emerged as a revolutionary approach in the realm of reproductive health, allowing expectant parents to ascertain paternity with minimal risk to both the mother and the fetus. Traditionally, paternity testing methods involved invasive procedures that posed potential health risks. However, advancements in genetic science have made it possible to obtain accurate results through non-invasive means. This article delves into the methodologies behind NIPPPT, elucidates the scientific principles involved, explores the benefits and limitations of these testing methods, and discusses the future implications for healthcare.
Understanding Non-Invasive Prenatal Paternity Testing Methods
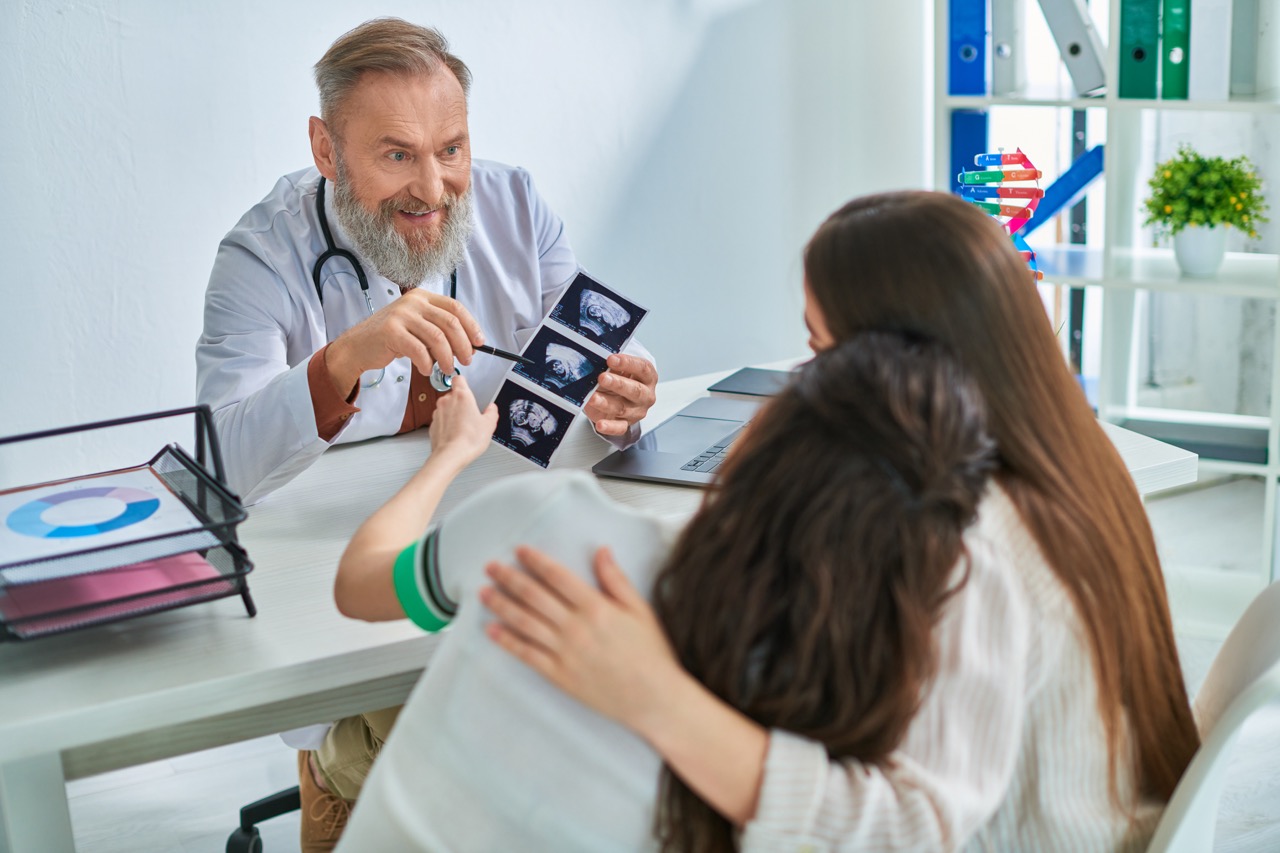
Non-Invasive Prenatal Paternity Testing primarily relies on the analysis of cell-free fetal DNA found in the mother’s bloodstream. This testing method is typically performed after the 8th week of gestation when sufficient fetal DNA is present. The procedure involves a simple blood draw from the expectant mother, which is then sent to a laboratory for analysis. By comparing the fetal DNA to the DNA of the alleged father, laboratories can determine the likelihood of paternity with a high degree of accuracy.
The process generally consists of extracting and amplifying DNA from the maternal blood sample. Specialized techniques, such as polymerase chain reaction (PCR), are employed to detect specific genetic markers associated with the fetus and compare them to those of the father. Various commercial services utilize different methodologies, but the core principle remains consistent: isolation of fetal DNA and comparative analysis with the potential father’s DNA.
Additionally, some testing providers offer advanced options like whole genome sequencing, which allows for a more comprehensive analysis of genetic material. This not only strengthens the paternity determination but also opens doors for discovering potential genetic conditions in the fetus. As a result, NIPPPT has quickly gained acceptance as a reliable and convenient alternative to traditional paternity testing methods.
The Science Behind Non-Invasive Testing Techniques Explained
At the heart of Non-Invasive Prenatal Paternity Testing lies the understanding of cell-free DNA (cfDNA). During pregnancy, a small portion of the fetus’s DNA is released into the mother’s bloodstream, predominantly coming from the placenta. This cfDNA carries genetic information that can be analyzed to confirm paternity. The technique hinges on the ability to isolate and amplify this fetal DNA while distinguishing it from the maternal DNA.
Laboratories employ sophisticated bioinformatics tools to analyze the sequencing data of the cfDNA. By identifying specific alleles—variations of a gene—scientists can create a genetic profile of the fetus and compare it to the profiles of both the mother and the alleged father. The examination focuses on single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs), which are variations at a single position in DNA. By assessing these SNPs, the testing can ascertain the likelihood that the alleged father is indeed the biological father of the child.
Furthermore, the accuracy of NIPPPT has been supported by numerous research studies, with results suggesting that the accuracy rate can exceed 99%. This impressive precision is largely attributed to the abundance of genetic markers that can be analyzed, allowing for robust comparisons between the fetal and paternal DNA. As testing methodologies continue to refine, we can expect further improvements in both accuracy and the scope of information available from these tests.
Benefits and Limitations of Paternity Testing During Pregnancy
The key benefits of Non-Invasive Prenatal Paternity Testing are rooted in its safety and convenience. Since the test is conducted through a simple blood draw, it eliminates the risks associated with invasive procedures like amniocentesis or chorionic villus sampling (CVS), which can potentially harm the fetus. Additionally, the non-invasive nature of the test means that it can be performed early in the pregnancy, providing peace of mind to expectant parents without unnecessary delays.
Another advantage of NIPPPT is its ability to provide results relatively quickly, often within a week. This timeliness is crucial for families who may need to make informed decisions about parenting, planning, or potential medical interventions based on genetic information. Moreover, in cases where there may be complications or uncertainties in relationships, NIPPPT can facilitate open discussions and planning for the future.
However, it’s essential to acknowledge the limitations of NIPPPT. While the tests are highly accurate, they are not infallible, and false positives or negatives can occur, albeit rarely. Additionally, the tests can only determine paternity and may not provide insights into other familial relationships or genetic disorders, which may be a concern for some parents. Furthermore, ethical considerations surrounding privacy, consent, and the emotional implications of paternity testing cannot be overlooked, necessitating careful contemplation before proceeding.
The Future of Non-Invasive Prenatal Testing in Healthcare
The landscape of Non-Invasive Prenatal Testing is poised for significant advancements in the coming years. As research and technology continue to evolve, we can expect improvements in test sensitivity and specificity, allowing for even more accurate paternity determinations. Furthermore, as the cost of genomic sequencing decreases, broader accessibility to these tests will likely become a reality, enabling more families to take advantage of the benefits offered by NIPPPT.
Integration with other prenatal testing methods holds considerable promise for the future. For instance, combining NIPPPT with non-invasive prenatal screening (NIPS) for genetic conditions could provide comprehensive insights into both paternity and fetal health. This holistic approach could revolutionize prenatal care by offering parents a deeper understanding of their child’s genetic makeup, thereby facilitating timely medical interventions if necessary.
Moreover, emerging technologies, such as artificial intelligence and machine learning, may enhance data analysis processes, improving the accuracy and efficiency of testing. As societal acceptance of genetic testing continues to grow, healthcare providers will likely incorporate NIPPPT into standard prenatal care practices, making it a routine part of family planning and reproductive health services.
Non-Invasive Prenatal Paternity Testing represents a significant advancement in reproductive medicine, providing families with vital information in a safe and convenient manner. While it offers numerous benefits, including accuracy and ease of access, it is essential for expectant parents to weigh the implications and limitations carefully. As technology progresses and further integration occurs within healthcare frameworks, NIPPPT is set to play an increasingly central role in prenatal care, shaping the future of family relationships and genetic understanding.