Paternity testing serves as an essential legal mechanism in various family law matters, particularly in the context of child support. The establishment of paternity is critical not only for the emotional and social dynamics of family life but also for the financial responsibilities that come with parenthood. As society continues to evolve, the role of paternity testing in legal systems becomes increasingly significant, particularly in ensuring that children receive the financial support they need from both parents. This article will delve into the various aspects of paternity testing, its influence on child support determinations, the legal implications that arise from established paternity, and the testing process itself.
Understanding Paternity Testing: A Key Legal Tool
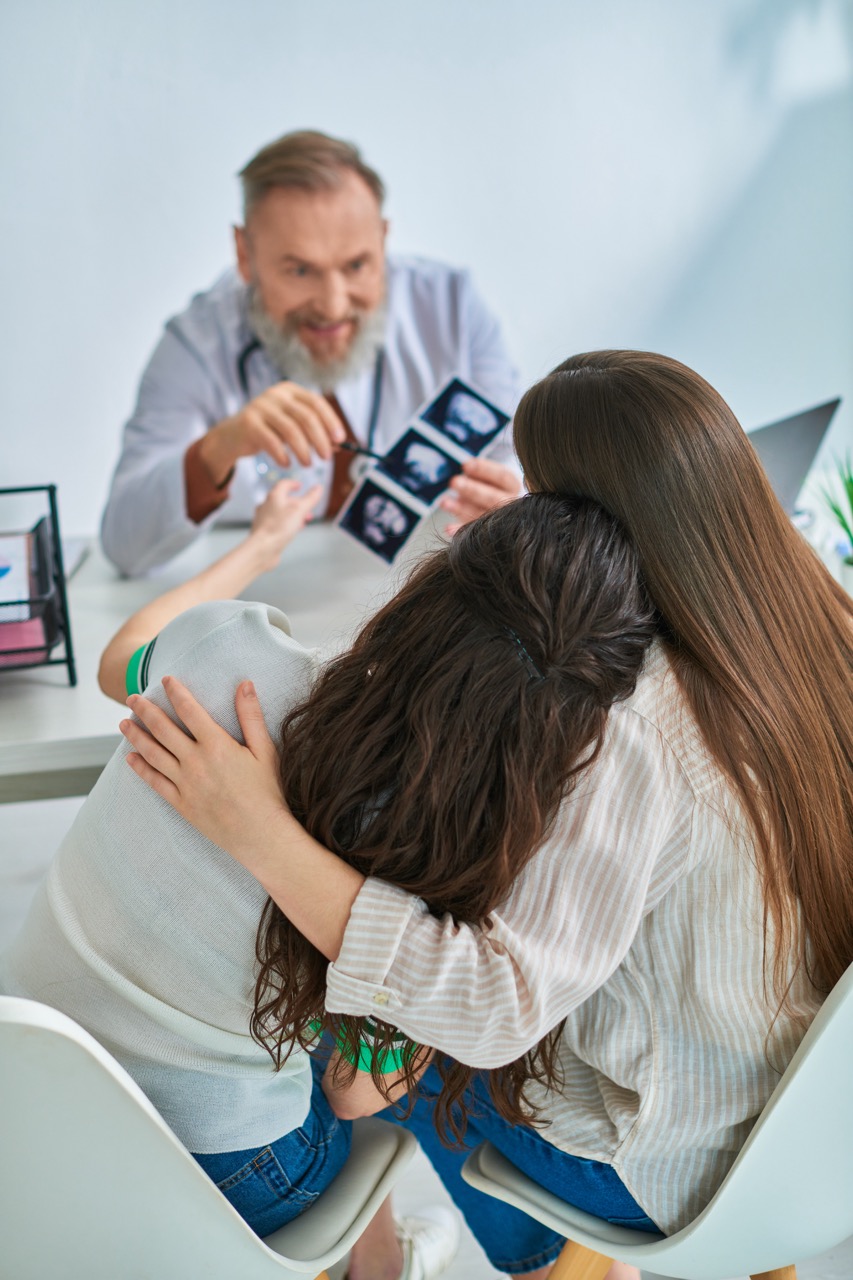
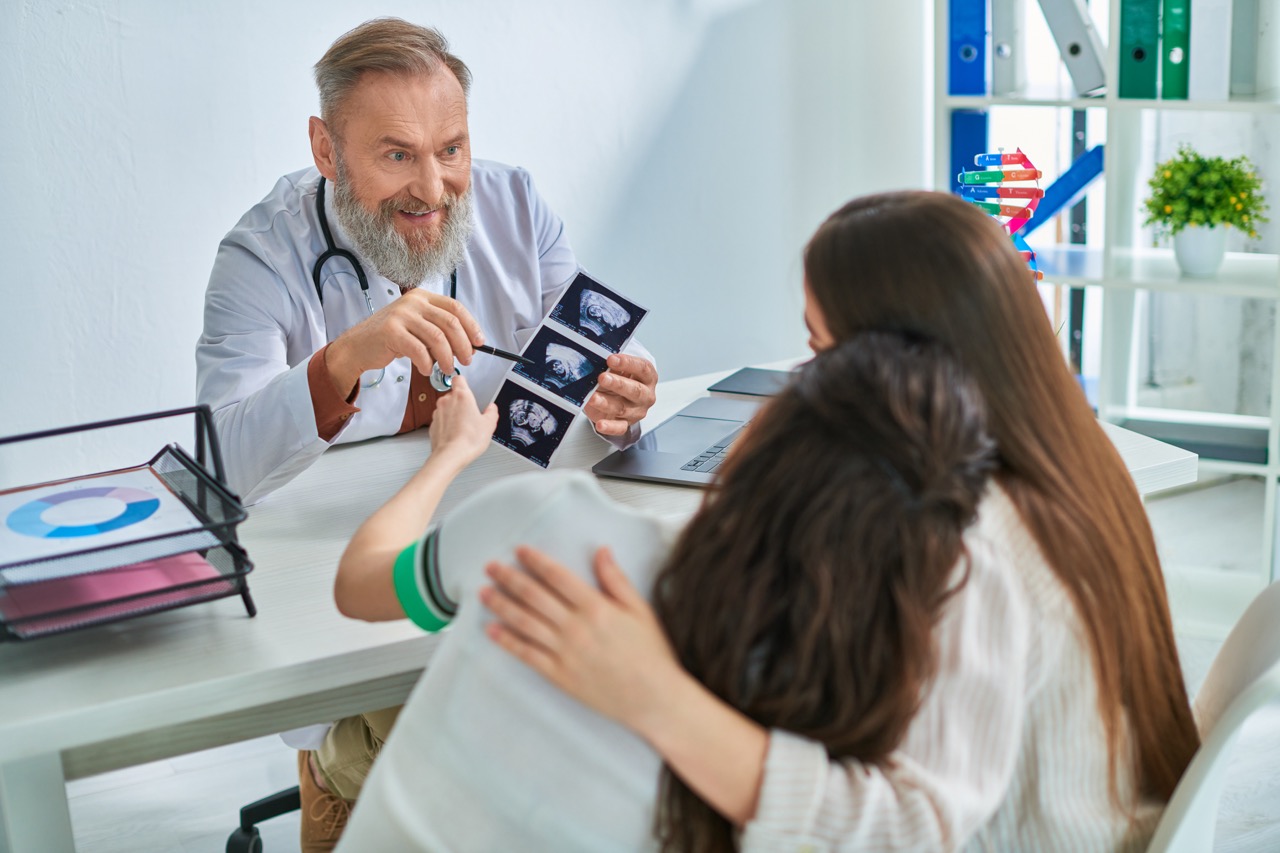
Paternity testing is a scientific method used to determine whether a man is the biological father of a child. The most common form of paternity testing involves DNA analysis, where samples from the child and the alleged father are compared to assess genetic similarities. This process is often initiated when there is a question of fatherhood, which can arise in various situations, including divorce, child custody disputes, or when parents are unmarried. The accuracy of modern DNA testing—often exceeding 99%—offers a reliable resolution to questions of paternity that may otherwise lead to prolonged disputes.
The legal ramifications of paternity testing are profound, as establishing paternity can significantly impact child custody and support issues. Courts typically require a legal proof of paternity to enforce child support obligations, making paternity testing not just a personal matter but a crucial element in the judicial process. In many jurisdictions, a child born to unmarried parents does not automatically have legal rights to financial support unless paternity is legally established. Thus, the role of paternity testing as a key tool in family law cannot be overstated; it serves as a gatekeeper for securing a child’s rights to support and care from both parents.
Moreover, the rise of paternity testing has implications beyond the courtroom. It also plays a role in public policy and social services. For instance, child welfare agencies often require proof of paternity when determining eligibility for benefits or services. By ensuring that children receive appropriate support from both parents, paternity testing contributes to overall societal welfare. As a legal tool, it has evolved to keep pace with changing family structures and societal norms, reinforcing its position as an indispensable element in safeguarding children’s rights.
How Paternity Tests Influence Child Support Determinations
The results of paternity tests directly influence how child support obligations are determined and enforced. When a man is legally established as the father of a child, he becomes legally responsible for financial support, which includes regular payments for the child’s living expenses, education, healthcare, and other needs. Courts typically use the information from paternity testing to assess financial responsibilities and ensure that both parents contribute equitably to the upbringing of their child. This is particularly critical in cases where the child’s welfare may be compromised due to the lack of financial support from one parent.
Child support calculations often consider various factors, including the income level of both parents, the needs of the child, and the standard of living they would have enjoyed had the parents remained together. The establishment of paternity allows for an accurate assessment of these factors, as legal fatherhood provides a clearer understanding of the financial resources available for child support. In situations where paternity has not been established, one parent may be left shouldering the financial burden alone, which can lead to significant disparities in child welfare.
Furthermore, paternity tests can also influence retroactive child support claims. If paternity is established after a child has been born, the court may order the biological father to pay support from the time of the child’s birth onwards, depending on the circumstances. This emphasizes the importance of timely and effective paternity testing, as delays can result in financial hardships for the custodial parent and the child. In essence, paternity testing serves as a critical lever in ensuring that child support obligations are fairly imposed and met.
The Legal Implications of Established Paternity in Support
Once paternity is legally established through testing, a range of legal implications ensues, particularly in relation to child support. The biological father is required by law to provide financial support for the child, which can include direct payments, medical insurance, and other related expenses. Courts are tasked with ensuring that child support orders reflect the best interests of the child, and established paternity provides a solid foundation for these decisions. This legal recognition is crucial for ensuring that children receive the support they need, regardless of their parents’ relationship status.
In addition to financial responsibilities, established paternity can influence custody and visitation rights. Fathers with established paternity may seek more involvement in their child’s life, which can lead to shared parenting arrangements. Courts generally favor arrangements that provide stability and nurture relationships between children and both parents. Consequently, paternity testing not only establishes a financial obligation but also opens the doors for fathers to engage in their child’s upbringing, fostering a more balanced family dynamic.
Moreover, the establishment of paternity can have long-term implications, including inheritance rights, access to medical history, and benefits such as social security or veteran’s benefits. Children benefit from knowing their biological parents and heritage, which can play a significant role in their identity and emotional well-being. In summary, the legal implications of established paternity extend well beyond child support, shaping the long-term relationship between parents and their children while ensuring that children’s rights and needs are prioritized.
The Process of Paternity Testing: What to Expect
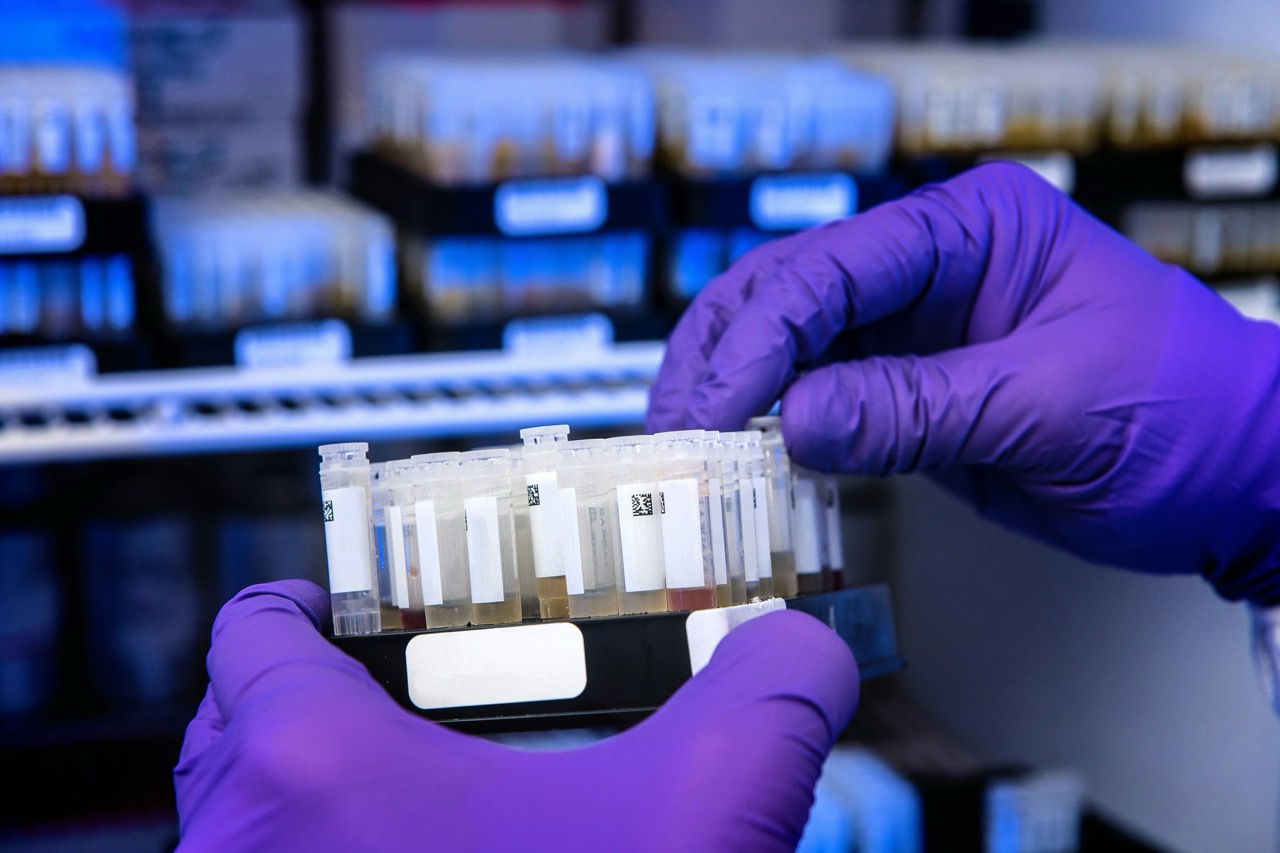
The process of paternity testing typically begins with the collection of DNA samples from the child and the alleged father. This can be done through a simple cheek swab, which is non-invasive and painless. In some cases, samples may be collected from the mother as well to provide additional context. Once the samples are collected, they are sent to a specialized laboratory where a DNA analysis is conducted to compare the genetic markers of the individuals involved. The process is usually straightforward and can often yield results within a matter of days.
After the testing is completed, the laboratory will provide a detailed report indicating whether the alleged father is the biological parent of the child. If paternity is confirmed, this information can be presented in court to establish legal fatherhood, thereby triggering the associated child support obligations. If paternity is disproven, the alleged father may be relieved of any financial obligations. It is important to note that the results of paternity tests can be contested, so individuals involved in these proceedings should consult with legal counsel to understand their rights and obligations fully.
Privacy and confidentiality are also major considerations in the paternity testing process. Reputable laboratories adhere to strict protocols to protect individuals’ information and ensure that results are disclosed only to authorized parties. This confidentiality is vital, as paternity testing often involves sensitive personal matters that can have profound emotional impacts on families. Understanding the process and its implications can help individuals navigate the complexities of paternity testing more confidently, ultimately leading to better outcomes for children and families involved.
Paternity testing plays a pivotal role in establishing child support and ensuring that children receive the financial backing they need from both parents. By clarifying biological relationships, paternity tests facilitate legal processes that protect children’s rights and promote equitable support from both parents. The implications of established paternity extend beyond mere financial responsibilities; they encompass emotional, social, and legal dimensions that shape family dynamics and individual identities. Understanding the intricacies of paternity testing empowers individuals to make informed decisions and reinforces the importance of shared parental responsibility in nurturing children. As societal norms continue to evolve, the significance of paternity testing in maintaining children’s welfare remains paramount.