Paternity testing has become a vital component in establishing parentage, particularly in surrogacy arrangements. As more families seek alternative paths to parenthood, understanding how paternity testing works in these situations is crucial. This article will explore the fundamental principles behind paternity testing, the role of genetic samples, relevant legal considerations, and the step-by-step process involved in conducting a paternity test within the context of surrogacy.
Understanding the Basics of Paternity Testing in Surrogacy
Paternity testing is a scientific method used to determine whether a man is the biological father of a child. In surrogacy cases, where a surrogate carries a child for intended parents, the determination of parentage can be complex. Typically, there are two primary types of surrogacy: traditional and gestational. Traditional surrogacy involves the surrogate using her own egg, making her the biological mother. On the other hand, gestational surrogacy involves an embryo created through in vitro fertilization (IVF), using the intended mother’s egg and intended father’s sperm, thereby solidifying the intended parents’ roles.
For intended parents—especially fathers—who seek to confirm their biological connection to the child, paternity testing serves as a reliable method. The test analyzes DNA from both the child and the alleged father to establish a genetic link. This process is straightforward, involving the collection of DNA samples, often through a simple cheek swab, followed by a comparison of genetic markers. The results can provide peace of mind to intended parents, reinforcing their legal and emotional ties to the child.
In surrogacy situations, the implications of paternity testing extend beyond mere biological relationships. The results can influence custody arrangements, parental rights, and even social dynamics within the family. As such, intended parents should approach paternity testing thoughtfully, considering both its emotional impact and its importance in establishing legal parentage.
The Role of Genetic Samples in Establishing Parentage
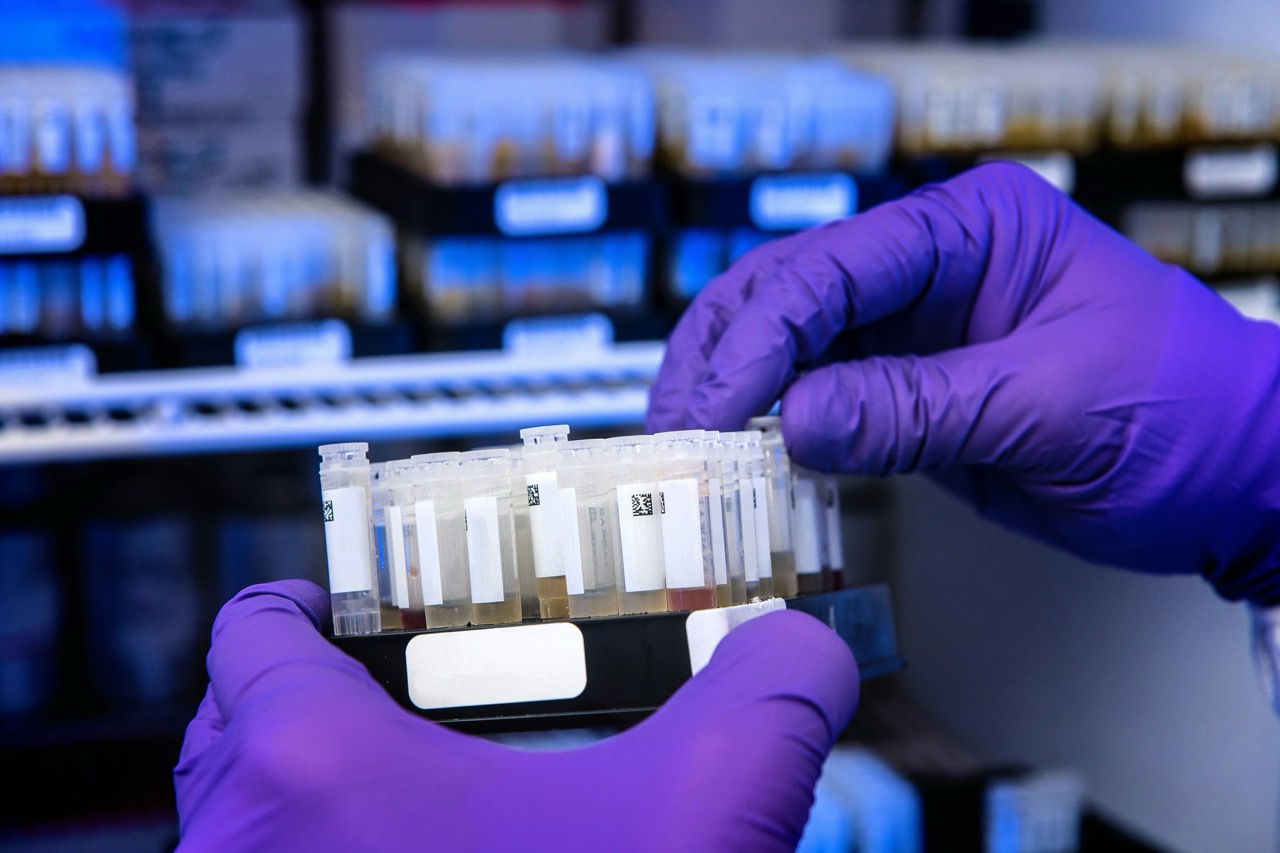
Genetic samples are the core component of paternity testing, as they provide the necessary data for analysis. In most cases, the primary sources of genetic samples include buccal swabs taken from the inside of the cheek or blood samples. The process of collecting these samples is non-invasive and straightforward, ensuring minimal discomfort for all parties involved. Once collected, the samples are sent to a certified laboratory, where they undergo rigorous testing to analyze specific genetic markers.
During the testing process, laboratories use advanced techniques such as polymerase chain reaction (PCR) to amplify the DNA segments extracted from the samples. This amplification allows for a detailed comparison of genetic markers between the child and the alleged father. A significant match in these markers indicates a high probability of paternity, while discrepancies can rule out a biological connection. Results are typically expressed as a percentage, with a probability of 99.9% or higher commonly accepted as conclusive proof of paternity.
The accuracy and reliability of genetic testing have transformed the landscape of parentage verification. In surrogacy cases, where emotional stakes are high, these results can play a pivotal role in confirming the biological ties between intended parents and their child. The undeniable clarity that genetic samples provide can alleviate uncertainties and foster a stronger bond between parents and their newborn.
Legal Considerations Surrounding Paternity Testing
Paternity testing in surrogacy is not only a scientific process but also a legal one. The results of a paternity test can significantly affect parental rights, especially in jurisdictions where biological connections are prioritized in legal matters. As such, intended parents should fully understand the legal ramifications of obtaining paternity test results prior to proceeding. It is essential to engage legal counsel familiar with family law and surrogacy in their specific jurisdiction.
In some cases, intended parents may need to establish their rights through legal documentation to ensure their status as the child’s legal parents. This process may involve court petitions, birth certificate amendments, and even adoption proceedings, particularly in traditional surrogacy arrangements where the surrogate is also the biological mother. The legal landscape can vary widely from one region to another, making it vital for intended parents to be informed about their rights and responsibilities.
Furthermore, confidentiality is a critical aspect of paternity testing in surrogacy. Legal agreements often stipulate how the results will be handled and who will have access to them. Protecting the privacy of all parties involved, including the surrogate, is paramount. This legal framework is designed to prevent disputes and ensure that the emotional well-being of the child and all parties involved is prioritized.
Step-by-Step Process of Conducting a Paternity Test
The process of conducting a paternity test in a surrogacy situation begins with the collection of genetic samples from the individuals involved. Typically, this includes samples from the child and the alleged father. The collection is usually performed by a trained professional in a clinical setting, often requiring only a simple cheek swab. This non-invasive method ensures that the procedure is quick and comfortable for all participants.
Once the genetic samples are collected, they are securely transported to an accredited laboratory specializing in paternity testing. The laboratory will then process the samples, extracting DNA and analyzing specific genetic markers. This analysis is conducted using established protocols to ensure accuracy and reliability. The laboratory typically takes several days to complete the testing and generate results, which will be communicated to the intended parents, often accompanied by an explanation of the findings.
Upon receiving the results, intended parents should consult with legal and medical professionals to understand the implications of the findings. If the test confirms paternity, intended parents may proceed with necessary legal steps to solidify their parental rights. In cases where the test yields inconclusive results or does not establish paternity, further discussions with legal counsel may be necessary to explore next steps or alternative arrangements. Ultimately, understanding the entire process ensures that intended parents can navigate the complexities of surrogacy with confidence.
In conclusion, paternity testing in surrogacy cases is a crucial step in establishing parentage and securing parental rights. By understanding the basics of paternity testing, the role of genetic samples, legal considerations, and the step-by-step process involved, intended parents can make informed decisions that align with their family-building goals. As the landscape of parenthood continues to evolve, being well-informed empowers families to create strong, bonded relationships with their children, irrespective of the challenges that may arise.