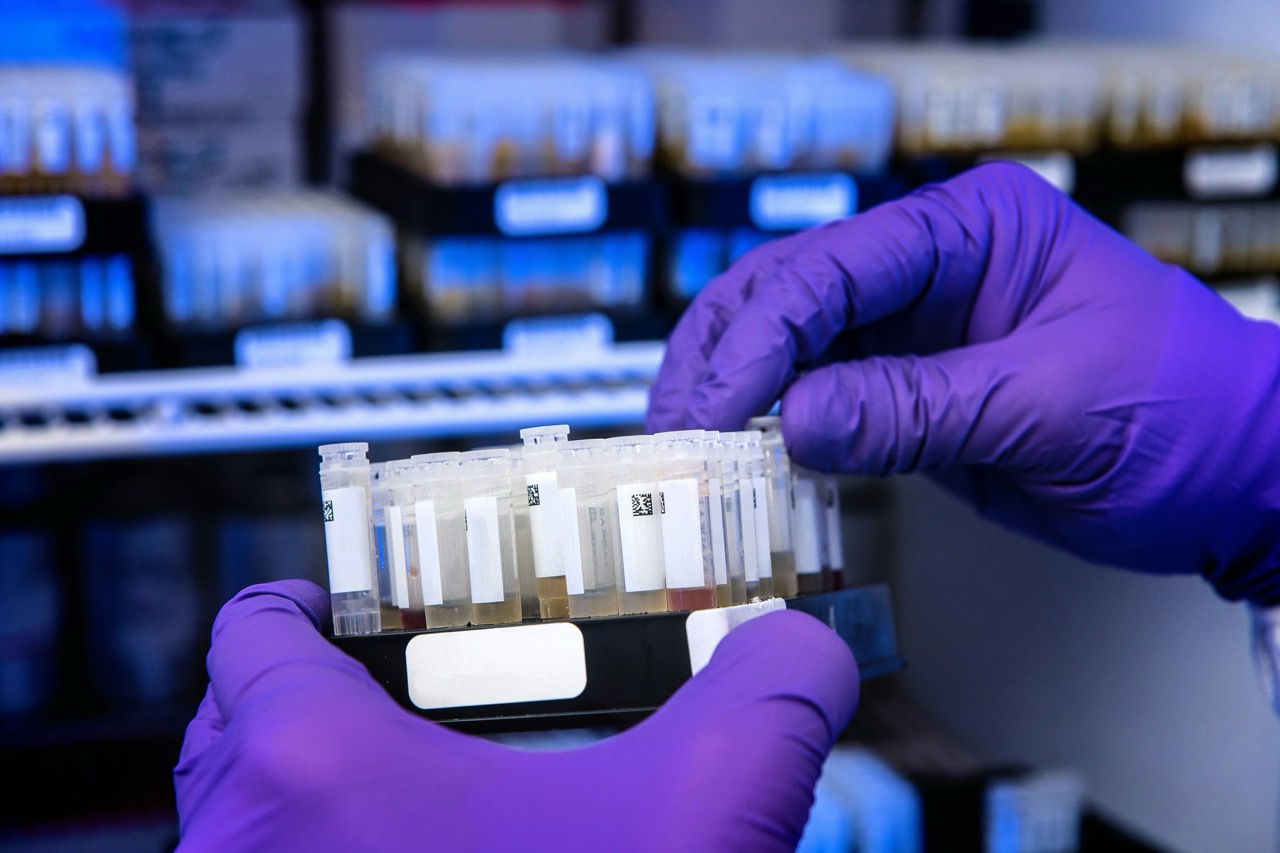
Laboratories serve as the backbone of scientific research, clinical diagnostics, and a myriad of industrial applications. Modern laboratories are not just about test tubes and pipettes; they are complex systems that ensure the accuracy and reliability of results that impact health, safety, and technological advancement. This article explores the multifaceted role laboratories play in ensuring accurate results, emphasizing critical functions, quality control, advanced technologies, and the commitment to continuous improvement.
Understanding the Critical Functions of Laboratories Today
Laboratories are integral to various fields, including healthcare, pharmaceuticals, environmental science, and forensic analysis. They provide a controlled environment where substances can be tested, measured, and analyzed with precision. Through rigorous experimentation and validation, laboratories help scientists and professionals gain insights that influence public health policies, product safety, and technological advancements. This foundational role is crucial, as the data generated in laboratories often serves as the basis for decision-making processes across numerous industries.
The processes in a laboratory are structured and standardized. This includes everything from sample collection and handling to testing protocols and data interpretation. By following established methodologies, laboratories ensure that the results obtained are not only accurate but also reproducible. This is particularly vital in clinical settings, where laboratory results can guide diagnoses and treatment plans, impacting patient outcomes significantly.
Moreover, laboratories serve as hubs of innovation. They are often at the forefront of developing new methods and technologies that enhance testing capabilities. Research and development within labs lead to improved diagnostics, more effective medications, and safer consumer products. As a result, laboratories contribute not only to immediate scientific inquiries but also to the long-term advancement of their respective fields.
The Importance of Quality Control in Laboratory Testing
Quality control (QC) is an essential aspect of laboratory operations. It refers to the systematic processes employed to ensure that laboratory results are accurate and reliable. QC includes regular calibration of instruments, validation of testing methods, and adherence to standardized protocols. By implementing robust quality control measures, laboratories can minimize errors and discrepancies that could lead to incorrect conclusions.
QC procedures involve multiple layers of oversight, from initial sample processing to final result reporting. Laboratories often utilize control samples—known quantities that serve as benchmarks for testing accuracy. By regularly analyzing these samples, laboratories can detect drifts in performance and take corrective actions before they affect patient care or product safety. This proactive approach not only safeguards the integrity of results but also builds trust among stakeholders, including medical professionals, patients, and regulatory bodies.
Additionally, the importance of external accreditation cannot be overstated. Laboratories often seek accreditation from recognized organizations, which provides an objective assessment of their quality management systems. This external validation not only enhances the credibility of the laboratory but also fosters a culture of continuous improvement and accountability, ensuring that quality is always prioritized.
Key Technologies and Techniques for Accurate Results
Advances in technology have revolutionized the laboratory landscape, enabling more precise and efficient testing methods. Automation, for instance, has streamlined many laboratory processes, minimizing human error and increasing throughput. Automated systems can handle repetitive tasks with greater accuracy and consistency, allowing laboratory personnel to focus on more complex analyses that require their expertise.
Molecular techniques, such as polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and next-generation sequencing (NGS), have become essential tools in fields like genetics and microbiology. These technologies allow for the rapid detection and quantification of nucleic acids, facilitating timely diagnostics and research. With the ability to analyze samples at a molecular level, laboratories can provide insights that were previously unattainable, enhancing the overall accuracy and reliability of results.
Moreover, data analytics and bioinformatics play an increasingly important role in modern laboratories. The integration of advanced algorithms and machine learning technologies allows for sophisticated data interpretation, enabling laboratories to identify trends, correlations, and anomalies with greater precision. As a result, laboratories can not only deliver accurate results but also contribute to predictive modeling and personalized medicine approaches, ultimately improving patient care.
Continuous Improvement: Ensuring Lab Results Are Reliable
Continuous improvement is a guiding principle for laboratories striving to ensure the reliability of their results. This involves regularly reviewing and updating protocols, adopting new technologies, and fostering a culture of feedback among laboratory personnel. By creating an environment that encourages innovation and collaboration, laboratories can stay ahead of emerging challenges and enhance their operational efficiency.
Staff training and development are also critical components of continuous improvement. Laboratories invest in ongoing education for their personnel, ensuring that they are well-versed in the latest techniques and technologies. Training programs promote a deep understanding of both the science behind testing and the importance of quality control measures, empowering laboratory staff to take ownership of their roles in delivering reliable results.
Furthermore, laboratories often engage in inter-laboratory comparisons and proficiency testing to benchmark their performance against industry standards. These assessments highlight areas for improvement and facilitate knowledge sharing among laboratories. By learning from one another and implementing best practices, laboratories can continuously refine their processes and maintain high levels of accuracy and reliability in their results.
In conclusion, laboratories play a vital role in ensuring accurate results across various sectors. Through critical functions, quality control, advanced technologies, and a commitment to continuous improvement, laboratories uphold the standards necessary for reliable testing. As scientific and technological advancements continue to evolve, so too will the practices within laboratories, allowing them to meet the demands of an increasingly complex world while maintaining the highest levels of accuracy.